LED Light Color Temperature: 5 Common misconceptions

LED Light Color Temperature: 5 Common misconceptions

LEDs light are everywhere from your smartphone to your desk lamp. Energy efficient and long lasting they are today’s smart choice. Still, a few myths surround them.
To bust the common misconceptions, it is crucial to understand the LED color temperature, how it works, and the role it plays in illuminating your surrounding space.
What Is Color Temperature?
In technical terms, color temperature refers to the “black-body radiator that emits light with a hue similar to the light source.”
In simple words, color temperature describes the light appearance from a light source. It could be warm or cool.
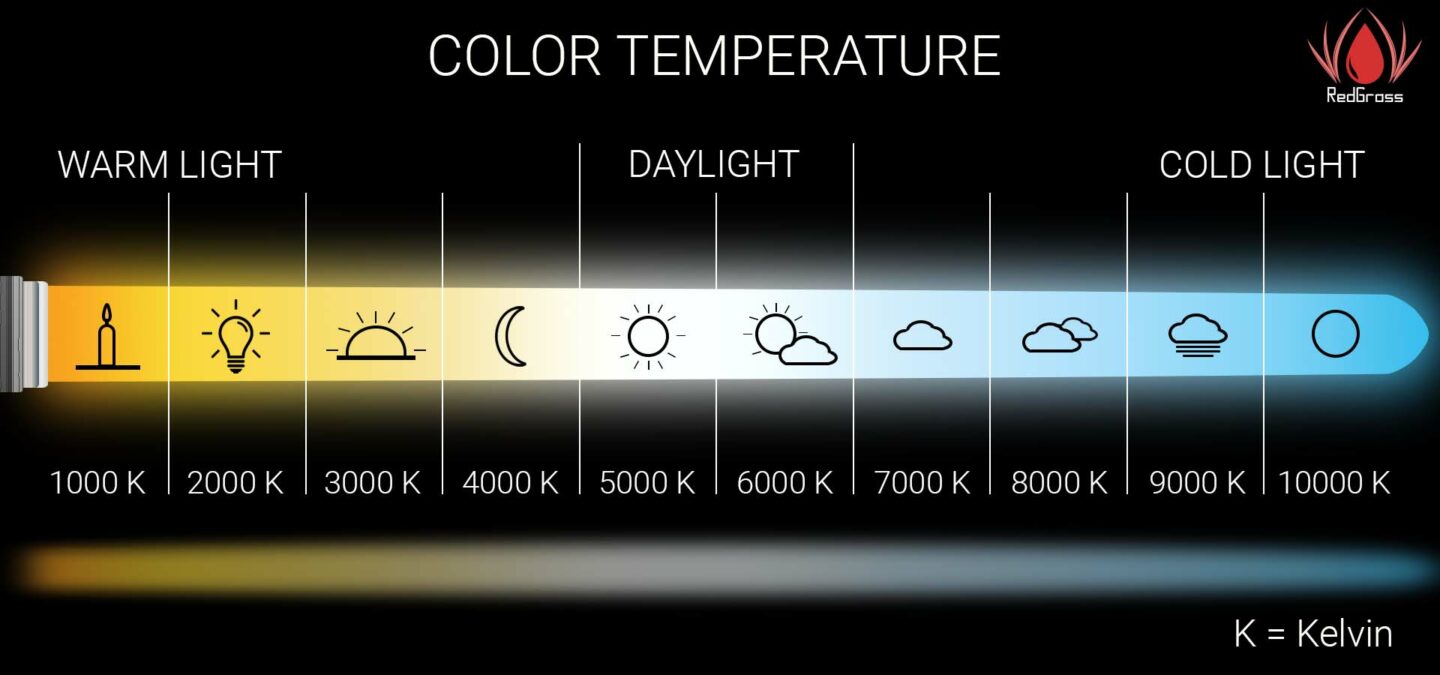
Note that the color temperature is typically measured in Kelvins (K). The higher the Kelvin, the bluer the light.
Wondering what determines the color temperature numbers? Let’s paint a picture.
Consider a jet-black object placed at room temperature. The item will appear black. However, when heated at 1500 degrees Kelvin, it will turn red. Heating it further at 2700K will turn it into a yellowish object.
At 4000K – 5000K, however, it’ll appear whitish and turn blueish at 5500K. That sums up how color temperature numbers work.
Generally, home fixtures have a color temperature on the kelvin scale of:
2700K (warm fluorescent)
3000k (warm white halogen)
3500k (household fluorescent)
Color temperatures around 4000K – 5000K known as daylight or neutral light are confortable for the eyes while boosting focus. Close to the color temperature of the sun at noon, it’s more suitable for commercial, professional or health center applications.
A light at 5000K might be suitable for sensitive tasks like painting, drawing, miniature painting, sewing, and other similar activities.
Importance of Color Temperature
The interplay of texture, light, and color has a significant impact on the overall look and feel of a space. Does the space feels warm or cold? You can change or tweak an ambiance with the right color temperature.
The color temperature of light can affect our mood and emotions. Warm lighting is often used in restaurants and bars to create a cozy, inviting atmosphere. Cool lighting is often used in offices and hospitals to help keep people alert and awake.
Warmer colors (like red and yellow) are perceived as more intimate and inviting, while cooler colors (like blue and green) are seen as more refreshing and energizing.
When it comes to your home, specifically your workspace, finding the right color temperature is imperative to help you be productive and comfortable.
Tips: According to our own experience, a color temperature of 4000K or 5000K is perfect for any workspace even at home.
What Is the Correct Color Temperature?
There’s no one-fits-all answer to this question. The ideal color temperature will depend on several factors. Mostly personal preferences but also the type of work you’re doing, the time of day…
If you’re not sure where to start, here are a few general guidelines:
A neutral to cool color temperature (4000-5500K) is generally best for daytime work. The higher end of this range will help you stay alert and awake, while the lower end will still provide a good color temperature without being too harsh on your eyes.
5000k is the recommended color temperature for any critical art, creative or miniature painting works, as the best neutral white.
A warm color temperature (2700-3000K) is the one often seen in lighting at our homes. Typical ceiling and lamp lights are at 2700K temperature scale.

Your personal preferences will also play a role in finding the right color temperature. For example, a higher color temperature may be best for you if you tend to feel more energized in cooler environments.
But some people prefer the warmer, cozy atmosphere of a lower color temperature. And if you’re particularly sensitive to light, you may find that a color temperature in the middle of the range is most comfortable.
No matter what color temperature you choose, it’s important to ensure your workspace is well-lit. A good rule of thumb is to have at least 50 lumens per square foot.
5 Common Myths About LED Light Color Temperature Debunked
LEDs have been around for decades, and many people know about their unique benefits, from affordability to lower energy consumption. Ironically, however, homeowners still hesitate to shift from incandescent bulbs to LEDs. A few believe LED lighting is too blue, while others believe LED’s light have a short lifespan.
The confusion exists due to a lack of understanding of the LED lights and the right color temperature. We’re here to unfold and debunk common misbeliefs about LED color temperatures.
1. LEDs Provide Unflattering White Light
A common misconception about LEDs is that they provide a very harsh, unflattering white light. This is simply not the case! In fact, with the right LEDs, you can get a warm, natural light that is perfect for any setting.
One of the great things about LEDs is that they can be yellowish to blue, depending on their color temperature.
For instance, cooler temperatures (6000K) tend to be bluer, while warmer temperatures are more yellow.(2700K)
That means that you can find the perfect light for any room in your house, from the bathroom to the bedroom. You can even find specialty bulbs that provide a nice, relaxing light for your living room or den.
LEDs are often used as an alternative to bright daylight as they perfectly mimic natural light (4000k to 5500k). They help enhance focus when working and their glow is cleaner and more flattering than the typical fluorescent bulbs.
2. The Bluer the Light Sources, the Cooler the Color Temperature
Here’s another myth about LED lighting. Most people believe that the whiter the light, the cooler the color temperature. The truth is the blueness of the light has nothing to do with the color temperature.
The color temperature of an LED bulb can be any color, including white. The higher the color temperature, the cooler or bluer the light.
Another thing to remember is that no color is warm or cool by itself. Instead, it’s relatively warmer or cooler than another color. So, for example, blue is cool because it has a lower color temperature than yellow.
So, when you see an LED bulb advertised as having a “cool white” light, it simply means that the phosphors used in the bulb produce blue light.
Keep in mind that the color of light is not the same as the color temperature. The color of light is determined by the wavelength of the light, while the color temperature is determined by the phosphors used in the light bulb.
3. A LED Light Has Poor Color Quality
A common myth about LED light is their poor color rendering quality. Well this one is tricky.
You need to understand the Color Rendering Index to understand this better. The Color Rendering Index (CRI) measures a light source’s ability to render colors accurately.
A high CRI means that the colors rendered by the light source are accurate, while a low CRI means that the colors are not rendered accurately.
Most LED lights have a CRI of 80, which is considered to be average. You can tell it is not great.
However with advancements in technology, LEDs are becoming more and more reliable. Some LEDs have a CRI of 95 or higher so pretty close to the Sun which makes LED excellent, close to perfect.
You must also ensure that the light has a wide color gamut. The color gamut is the range of colors that a light source can produce. A wide color gamut means that the light source can produce a broader range of colors, which is essential for rendering colors accurately.
4. LED Emits Blue Light Bad For Eyes
Let’s understand the concept of blue light. What is it? Blue light is a type of visible light with a shorter wavelength than other colors. It is scattered more easily than other colors, which is why the sky looks blue.
Electronic screens, such as computers, phones, and TVs, also emit blue light. This has led to concern that too much exposure to blue light may be harmful.
Sufficient research shows that blue light disrupts our circadian rhythm.
The circadian rhythm is our natural sleep-wake cycle. It’s regulated by the release of a hormone called melatonin.
Melatonin is primarily released at night, and it makes us feel sleepy. Exposure to blue light at night suppresses the release of melatonin and makes it harder to fall asleep.
Very long direct exposure of blue light is also thought to damage eyes. We are talking of years of exposure without any safety protocole.

The circadian rhythm is our natural sleep-wake cycle. It’s regulated by the release of a hormone called melatonin.
Melatonin is primarily released at night, and it makes us feel sleepy. Exposure to blue light at night suppresses the release of melatonin and makes it harder to fall asleep.
If you’re having trouble sleeping, it’s essential to limit your exposure to blue light in the evening. You can do this by avoiding electronic screens for a few hours before bed.
You can also buy blue-light-blocking glasses, which filter out blue light and may help you sleep better.
5. Higher the Color Temperature, More Powerful the Lights
Here’s a widespread misconception that’s mainly due to the lack of understanding of how light works.
A high color temperature doesn’t mean the lamp will have a high light intensity.
When the degrees Kelvin are higher, the color temperature of a light bulb is bluer and may seem ‘brighter’ as compared to lower Kelvin reading. For the power or light intensity of the light, you have to consider Lumen. In the lighting world, a light bulb’s brightness is measured in lumens.
So, to put it simply, a light bulb with a Kelvin reading of 4000 will not be ‘doubly bright’ as one with a Kelvin reading of 2000. People tend to believe this because our eyes are much more sensitive to blue light, which is at the higher end of the Kelvin spectrum.
The human eye is most sensitive to light in the yellow-green region of the visible spectrum, with a peak of around 555 nanometers. However, the blue end of the spectrum is where our eyes are most sensitive to changes in light intensity.
Even if an LED lighting has a higher Kelvin reading, it doesn’t make it any brighter than an incandescent light bulb with a lower Kelvin reading. The lumens are what matter when it comes to brightness, not the color temperature, ie. the Kelvin rating.
LUMEN:
One lumen is defined as the amount of light emitted in a unit solid angle of one steradian from a uniform point source with an intensity of one candela.
CANDELA:
A candela is a unit that measures the light emitted in a specific direction. So, even if a light bulb has a higher Kelvin reading, it doesn’t necessarily mean it emits more light.
How to Choose the Correct LED Color Temperature For You?
Color temperatures can be a bit complicated to understand. So, you might need help choosing the right light sources for your home.
Fortunately, LED lighting is available in different color temperatures. So, you’re spoilt for choice. First, here’s a summary of the color temperatures:
1800K: Candlelight
2500K: Sunrise and Sunset
3000K: Light bulb
3500K: Morning or Evening sun
4000K: Moonlight
5000-5500K: Midday sun
6500K: Cloudy sky
10000K: Clear sky
As you can see, the color temperature of light sources can vary greatly. The list above is a guide to help you make your choice.
Color Temperatures of LED Lights
In terms of an LED lighting source, here’s what you need to know about the color temperatures:
3600K-4500K: Warm
4600K-4900K: Morning daylight
5000K-5500K: Neutral daylight
5600K-6400K: Cool daylight
6500K+: Ultra daylight
If you need something warmer, the 1900K-3500K is a good option. Meanwhile, light sources in the 1500K-1800K have a candlelight color temperature.
Now that you understand the color temperatures and their corresponding lights, you can start considering the factors you need to focus on to find the right bulbs.
Ambiance
First and foremost, you must focus on the ambiance you want to create in your home. The atmosphere you choose should be based on your personal preferences.
For example, if you want to create a romantic ambiance, you might want to focus on light sources with a lower color temperature.
On the other hand, if you’re looking for a light source to help you concentrate, get bulbs with a higher color temperature. Of course, you can get multiple light sources to set the ambiance for different parts of your house.
Workspace

If you have a home office or study, you must ensure that your light source doesn’t strain your eyes. So, choosing the right color temperature is imperative in this case.
To do this, get LED lights with a higher color temperature. These will help you stay alert and focused while you work.
Moreover, if you suffer from migraines, you might want to get bulbs with a lower color temperature. Again, it is because bright lights can trigger migraines in some people.
Color Rendering Index
The color rendering index (CRI) is a measure of how well a light source displays colors. A CRI of 100 is the highest possible value, which means that the colors appear natural.
In general, you should get light bulbs with a CRI of 80 or higher. However, if you need light for tasks that require color discrimination, then you should get light bulbs with a CRI of 90 or higher.
For example, the CRI is important for people who work in the makeup industry. If you’re a makeup artist, you need to be able to see the colors accurately so that you can apply makeup flawlessly.
In this case, getting light bulbs with a CRI of 95+ would be ideal.
In addition, the light is flicker-free and glare-free. So you can work comfortably without getting your eyes strained. Since there are two options (recommended 5000 Kelvin and alternative 6500 Kelvin), you can choose the light color temperature that suits you best.
Beam Angle
The beam angle is the angle at which light is emitted from the light source. The larger the angle, the wider the beam of light.
Opt for light bulbs with a beam angle of 120 degrees or less. A smaller beam angle is ideal for task lighting because it offers a focused beam of light.
Blue Light Emission
You want to ensure that the light bulbs you choose don’t emit blue light. Blue light is harmful to your eyes and can cause digital eye strain.
The Redgrass R9 Desk Lamp limits blue light emission. So, you can be sure that your eyes are protected from the harmful effects of blue light.
Final Words
Summing up, color temperature is an interesting concept that has a variety of applications. From photography to lighting, understanding color temperature can help you create the results you want.
In terms of LED lighting, color temperatures are imperative to understand because different color temperatures emit different light hues. Above, we have mentioned some common myths about LED light color temperature.
Whether you are looking for cool or warm white light, make sure to pay attention to the color temperature of the LEDs. No matter what color temperature you choose, it’s important to ensure your workspace is well-lit, make sure to check also Lumens, Color Rendering Index,… and other technical features such as flicker-free or no glare, especially for precision tasks, to select the appropriate LED lamp.